 Click to visit the previous dinosaur bio
Click to visit the previous dinosaur bio
 |
|
 |
|
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Chordata
Class: Sauropsida
Superorder: Dinosauria
Suborder: Sauropodomorpha
Family: Plateosauridae
Genus: Sellosaurus
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|

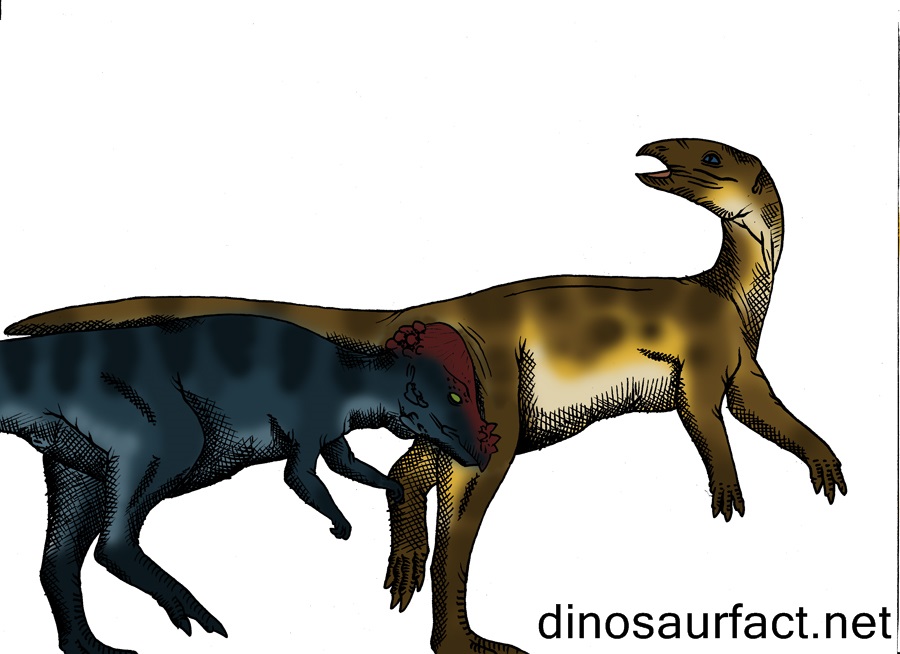
The Sellosaurus was a prosauropod dinosaur whose existence is controversial even today. Many scientists believe that the Sellosaurus and the Plateosaurus was the same dinosaur. Others contest the Sellosaurus preceded the Plateosaurus; the two may have had a common ancestor or the Plateosaurus could have evolved from the Sellosaurus.
Although the exact taxonomic classification of the Sellosaurus is fickle, its other characteristics are well accepted. It was a basal sauropodomorph dinosaur that lived in the Norian age of the Triassic period. It was extant about 218 to 210 million years ago. The fossils of the organism were discovered in Germany.
The Sellosaurus was a herbivorous dinosaur. Its adult size was about 4 to 7 meters in length. Its height was about 3 meters. Its weight possibly could have been between 300 to 600 kilos.
Nomenclature
The word ‘sela’ translates to ‘saddle’ in the Greek language. The suffix ‘-saurus’ indicates ‘lizard’ in Latin. Thus, the term ‘sellosaurus’ signifies ‘saddle-like lizard’.
The name ‘sellosaurus’ was suggested by paleontologists Peter Galton and Robert Bakker in the year 1985. It may have been due to the typical hunched posture of the Sellosaurus.
The binomial name Sellosaurus gracilis is derived from the Latin word ‘gracile’ which means ‘graceful’.
Classification
The classification of the remains the Sellosaurus has been a confusing endeavor.
- Friedrich von Huene was the first scientist to examine the remains of the Sellosaurus. He classified these fossils as those of the Paleosaurus or the Thecodontosaurus. Later they were ascribed to the Efraasia.
- Many years later scientists Galton and Bakker reclassified the remains to a separate genus ‘Sellosaurus’ as they were discovered lower than the other fossils
- However, Adam Yates in 2003 shifted the fossils of the Sellosaurus gracilis to the genus Plateosaurus and deemed that the species gracilis belonged there.
The most recent studies indicate that the Sellosaurus gracilis is indeed a type species of the Plateosaurus.
- Opponents of this hypothesis maintain that the fossils of the Sellosaurus were older than those of the Plateosaurus. They believe that the large differences in size of the Paleosaurus may indicate the presence of different genera of dinosaurs.
- The Sellosaurus was distinctly smaller than the Plateosaurus engelhardti. The skull and teeth of the Sellosaurus are also considered different as compared to the Plateosaurus.
- Furthermore, the bones of the Plateosarus were discovered in large numbers while those of the Sellosaurus were scanty.
Until more fossils are found, this debate may never rest.
Discovery of fossils
The remains of the Sellosaurus were excavated in the early 1900s from the Lowenstein Formation of the Keuper group of present day Germany. They were found in the lower Norian region of the formation.
Types of fossilized bones discovered
A substantial number of bones of the Sellosaurus were discovered in the Lowenstein formation. These included parts of the skull and teeth. Long bones of the front and hind limbs were also uncovered. A few vertebrae and portions of the pelvic girdle are also attributed to the Sellosaurus.
Current location of fossils
The remains of the Sellosaurus gracilis are presently housed and displayed in the State Museum of Natural History in Stuttgart, Germany.
The Lowenstein Formation
The Lowenstein Formation is natural geological structure located in Germany. It is part of the Keuper group of rock formations. It is name ‘Stubensandstein’ in Baden-Wurttemburg and ‘Burgsandstein’ in Bavaria.
- The fossils found in the Lowenstein Formation date back predominantly to the Norian age and occasionally to Rhaetian age of the Triassic period.
- A rich diversity of rocks is seen in this formation. They include sandstone, feldspar, clay, dolomite and many more.
- The average thickness of the Lowenstein Formation is 130 meters. Its depth reduces drastically at the Stubensandstein end.
- Many vertebrate and invertebrate fossils were excavated in the Lowenstein Formation. The prehistoric tortoise Proganochelys was found here. Remains of the Murrhadtia were also discovered in this formation.
- Dinosaur species such as the Sellosaurus, Plateosaurus and the Efraasia were unearthed in the Lowenstein formation.
- The sandstones of this formation were used to erect buildings in the past.
Friedrich von Huene
Friedrich von Huene, born Friedrich Richard von Hoinigen, was a German paleontologist and biologist. He had worked extensively in the early twentieth century towards the identification and classification of dinosaur species.
He is credited with defining upper taxonomic groups such as Prosauropoda and Sauropodomorpha. He also generated many sub classifications and genera for the dinosaur species he examined. Although many of these groups are no longer used, he was the pioneer in developing intricate classifications species, a practice followed and appreciated even today.
Along with dinosaurs, von Huene had also worked with other vertebrates. He discovered the remains of the Prestosuchus, a prehistoric crocodilian, in the Paleorrota Park.
von Huene has been a very key figure in the vertebrate paleontology arena.
Physical features
- The Sellosaurus was a moderately sized dinosaur. It grew to the length of 18 to 20 feet from snout to tail. Its height was about 7 to 8 feet.
- It walked on two feet, i.e. it was bipedal.
- The forelegs of the Sellosaurus were smaller than its hind legs. Certain scientists believe that it had a flexible thumb which it used for grasping and self-defense.
- The Sellosaurus has strong hind legs, as indicated by the muscle attachments on its long bones.
- Its neck and tail was long and flexible like other early sauropodomorphs.
Habits and habitat
The Sellosaurus was a herbivore. It is believed to have fed on soft vegetation due to the shape and assembly of its teeth.
Its habitat consisted of wooded areas. These were interspersed with water bodies and marshes. The climate of its environment was hot and dry.
Related and coexisting species
The Sellosaurus is assumed to be very closely related to the Plateosaurus. Many scientists believe that it was a smaller variant of the Plateosaurus.
The Efraasia could also have been related to the Sellosaurus.
The Sellosaurus may have coexisted with the above mentioned dinosaurs, along with the many theropod dinosaurs of the late Triassic against whom it had to defend itself.
Final notes of the Sellosaurus
The existence of the Sellosaurus as a separate genus is suspect. Much of the existing evidence points out that the Sellosaurus gracilis was a sub species of the Plateosaurus.
Index
Extinct Profiles
 Triassic Dinosaurs
Triassic Dinosaurs Jurassic Dinosaurs
Jurassic Dinosaurs Cretaceous Dinosaurs
Cretaceous Dinosaurs Pterosaurs
Pterosaurs Marine Reptiles
Marine Reptiles Dinosaur Extinction
Dinosaur Extinction