 Click to visit the previous dinosaur bio
Click to visit the previous dinosaur bio
 |
|
 |
|
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Chordata
SuperOrder: Dinosauria
Order: Theropoda
Family: Dromaeosauridae
Genus: Dromaeosaurus
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
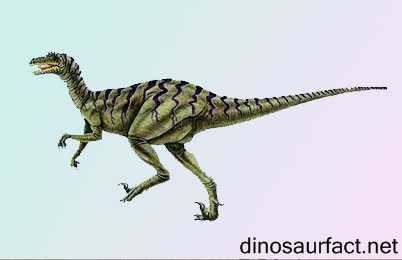
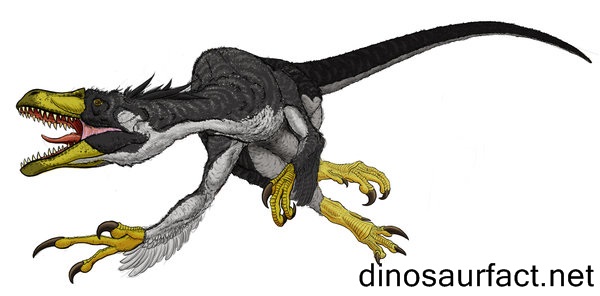
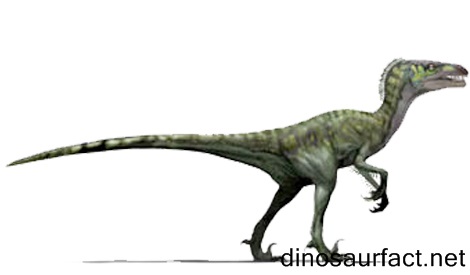
The Dromaeosaurus, as the name suggests, is the type genus for family Dromaeosauridae. It was a small sized dinosaur that lived on the earth in the late Cretaceous Period. The timeline of its existence was deduced to be about 78 to 72 million years ago. Thus, it was present in the Campanian as well as Maastrichtian ages. It likely became extinct right before the Cretaceous Paleogene extinction event, but it was indeed succeeded by other dromaeosaurids.
Not a lot of fossil evidence is ascribed to this dinosaur. Much of the information about it was deduced from studying other dromaeosaurs. The length of the Dromaeosaurus is judged to be about 1.8 meters from snout to tail. Its weight is presumed to be around 30 to 35 pounds. It is believed that the Dromaeosaurus did indeed possess feathers like most of its peers, but there no unequivocal evidence proving this. But it is known with certainty that it was carnivorous.
The fossils of this dinosaur were unearthed in Canada as well as the United States, indicating that it probably evolved in the northernmost regions of North America.
Etymology
The name Dromaeosaurus is inspired from the Greek language. The term 'dromeas' is the Greek word for 'runner'. The suffix 'saurus' is derived from the word 'sauros', which is Greek for 'lizard'. Thus, the name of this reptile roughly translates to 'the running lizard'. At the time of the discovery of the Dromaeosaurus, very few similar dinosaurs were described. And its holotype consisted majorly of foot bones. Hence such a name was chosen for it.
The specific name D. albertensis honors the Alberta region of Canada, where the bones of the dinosaur were first found.
The christening of the remains was done by William Matthew and Barnum Brown in 1922.
Discovery of fossils
- The remains of the Dromaeosaurus were first discovered by paleontologist Barnum Brown in the year 1914. He discovered them along the banks of the Red Deer River of Alberta. Brown had found many fossils during that expedition along the Red Deer and so those of the Dromaeosaurus got ignored slightly as the fossils he found were better preserved.
- The holotype consisted of a partial skull, the mandible, hyoids, a single metacarpal and few foot bones.
- After these initial findings, a few more isolated bones were recovered from the Dinosaur Provincial Park in Alberta.
- The Hell Creek Formation and Lance Creek Formation of Montana, United States, have yielded individual tooth fossils which have since been classified under the genus Dromaeosaurus.
Nature of fossils
The skull of the Dromaeosaurus was about 25 cms long. It was shorter proportionately as compared to the other dromaeosaurids, but it was much more sturdy and powerful. The teeth of this dinosaur were quite large proportionately too, and very sharp. But they had shown a lot of wear and tear. The upper jaw had only nine teeth.
The feet of the dinosaur showed the second large claw that was typical of all dromaeosaurs. The function of this adaptation is still debated by researchers.
No feather fossils have yet been ascribed to the Dromaeosaurus.
Classification
- When the fossils of the Dromaeosaurus were first discovered, there were very few similar dinosaurs defined to compare them with. The only information that was established about the remains was that they belonged to a meat eating dinosaur and that the skull had similar dimensions to the dinosaurs of that taxon.
- Due to this. Brown and Matthew classified it under family Deinodontodae. This taxon is currently called the Tyrannosauridae and it contains the famous Tyrannosaurus. They defined a new subfamily for these species, the Dromaeosaurinae.
- In the year 1969, scientist John Ostrum noticed the similarity between the Velociraptor, Deinonychus and the Dromaeosaurus. Based on this, he coined a new family, Dromaeosauridae and classified all the above mentioned dinosaurs within it.
- Since then, many similar dinosaurs have been discovered and defined.
- Apart from the type species D. albertensis, many more subspecies have been defined, like the D. explanatus and the D. falculus. But the validity of these species is doubtful. Some of them could be synonymous with the D. albertensis while others may just belong to completely new dinosaurs.
Physical characteristics
- The Dromaeosaurus was small sized, lean dinosaur. Its length (including tail) was around 6.5 feet but its weight was only 15 to 18 kilos.
- The jaw of the dinosaur had a much stronger bite force proportionally as compared to the dromaeosaurids. This, combined with the wear and tear on the teeth, indicate that the jaw was used to subdue prey on the basis of sheer strength. The teeth may have been used for grip rather than for biting or tearing.
- The forelegs of the Dromaeosaurus likely consisted of three digits.
- Each of its hind legs had four phalanges. The second consisted of large claw which was likely suspended on the air while walking.
- The tail of the dinosaur was long and slender.
- The most probably possessed an exoskeleton on feathers.
Habits and habitat
- The Dromaeosaurus was a bipedal dinosaur. It is difficult to say whether it could actually run very fast, as its name may lead one to believe.
- It body was not adapted for flying, so feathers or not, it was most definitely terrestrial.
- The diet of this dinosaur was carnivorous. Based on its size, it could only likely trap smaller reptiles and mammals. It is also possible that the Dromaeosaurus was a scavenger, eating off the leftovers of larger dinosaurs or just eating dead animals.
- The function of the claw on its leg is not fully understood. Some scientists believe that it was used to rip its prey apart. The more recent studies have said that it could have been an adaptation for climbing rocks.
- Very few fossils have been ascribed to the Dromaeosaurus as compared to other dromaeosaurs. This may mean that its numbers in the Cretaceous North America were limited.
- No other information is available about its nesting or reproductive habits.
- The habitat of the Dromaeosaurus consisted of grasslands and woodlands.
Related and coexisting species
The familial relationships of the Dromaeosaurus are not clearly known but paleontologists believe it was related to the Achillobator and the Utahraptor. It probably shared its habitat with the Tyrannosaurus, Triceratops, Struthiomimus, etc.
The final notes
The discovery of the Dromaeosaurus was key in understanding the ‘raptors’. Its skull is still one of the best preserved dromaeosaurid skulls to ever be found.
Just for fun we have a soundclip available for you to hear what a Dromaeosaurus could've sounded like. Click to the Dinosaur Sounds area to hear it. Please note that the dinosaur sounds are only for entertainment and are not an actual fact.
Index
Extinct Profiles
 Triassic Dinosaurs
Triassic Dinosaurs Jurassic Dinosaurs
Jurassic Dinosaurs Cretaceous Dinosaurs
Cretaceous Dinosaurs Pterosaurs
Pterosaurs Marine Reptiles
Marine Reptiles Dinosaur Extinction
Dinosaur Extinction